A Unique Introduction:
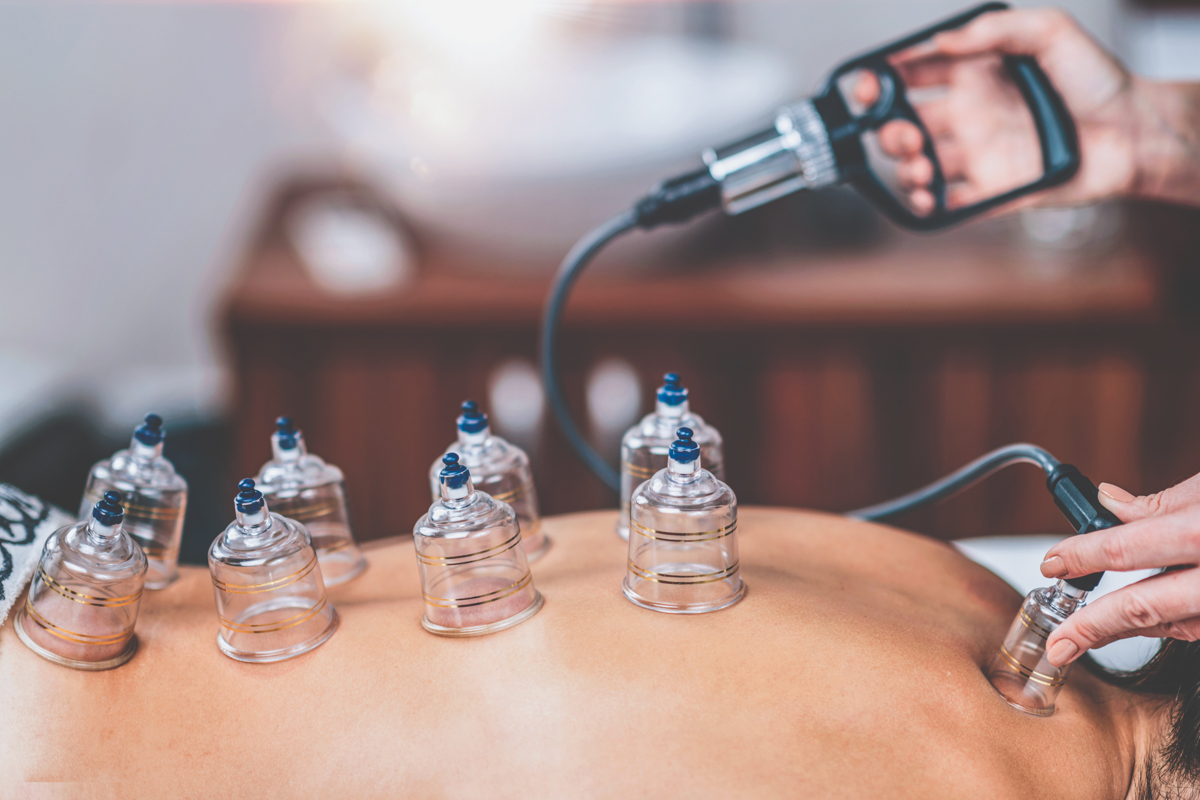
In the realm of modern medicine, where the challenges of autoimmune diseases continue to grow, cupping therapy emerges as a unique approach worthy of deep exploration. Far from being merely a traditional practice, cupping holds promising potential in supporting patients with autoimmune diseases, through mechanisms that may go beyond conventional understanding of treatment. This article offers a unique perspective on the role of cupping, supported by some preliminary research, while emphasizing the importance of integration and continuous scientific inquiry.
Cupping Therapy: A Potential Window for Modulating the Autoimmune Response?
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by the immune system unjustifiably attacking the body’s healthy tissues. Here lies a unique question: Could cupping therapy, which impacts circulation and inflammation, play a role in regulating immunity and reducing this self-attack? Some studies suggest that cupping may influence the immune response in complex ways, potentially offering benefits in certain aspects of autoimmune diseases.
Potential Mechanisms of Cupping Therapy in the Context of Autoimmunity:
Although research is still in its early stages, several potential mechanisms may explain cupping’s impact on autoimmune diseases:
Reducing Systemic Inflammation: It is believed that cupping, particularly wet cupping, may help reduce levels of certain inflammatory substances in the body, which play a key role in exacerbating autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
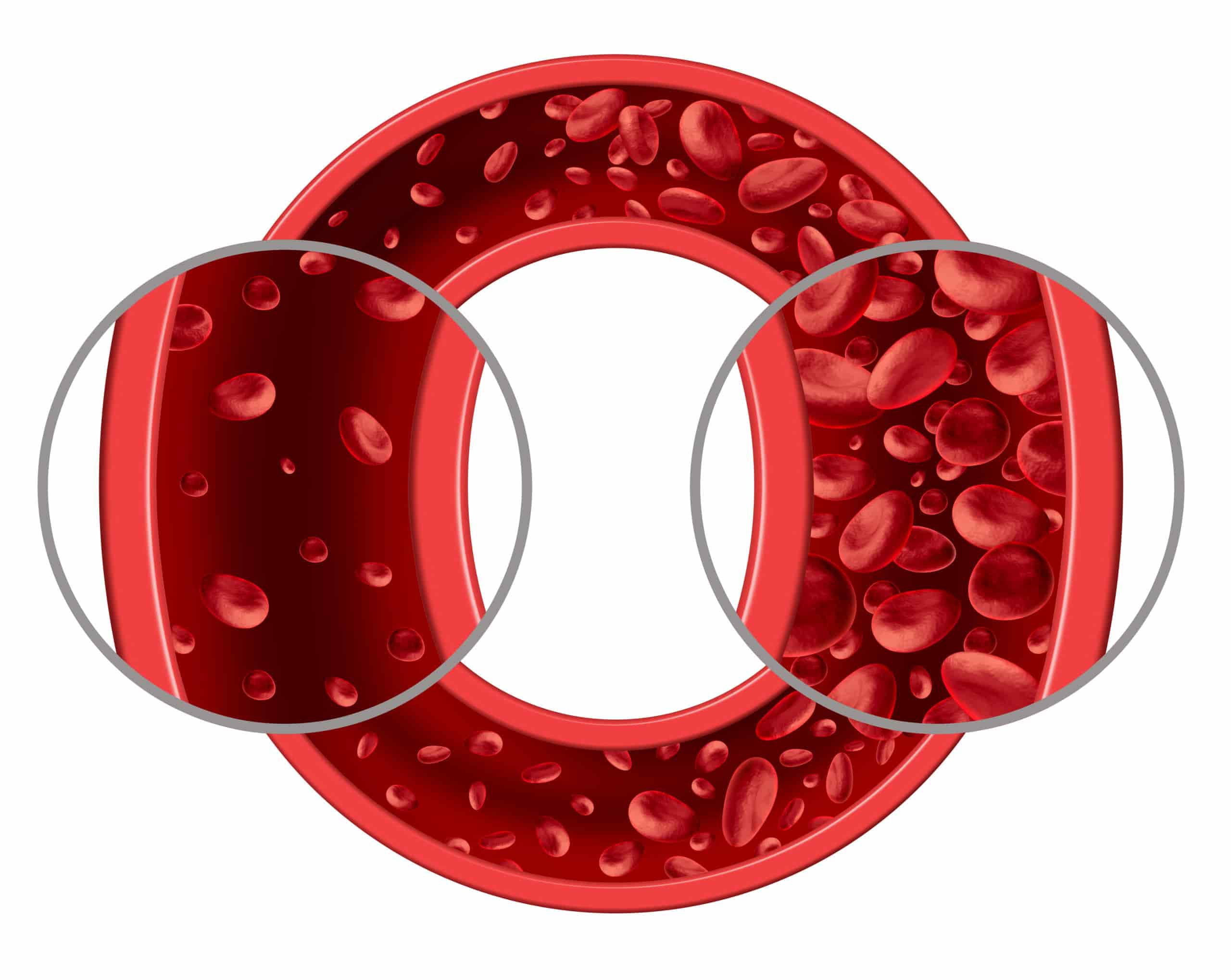
Improving Circulation and Detoxification: Cupping may contribute to enhancing blood flow and removing substances that could contribute to inflammation and worsen symptoms. This improvement in circulation may help alleviate the inflammatory conditions associated with autoimmune diseases.
Modulating Immune Cell Response: Some studies indicate that cupping may influence the activity of certain immune cells, which could help regulate the excessive immune response seen in autoimmune diseases. By potentially modifying the immune system’s activity, cupping might assist in alleviating some of the symptoms of these diseases.

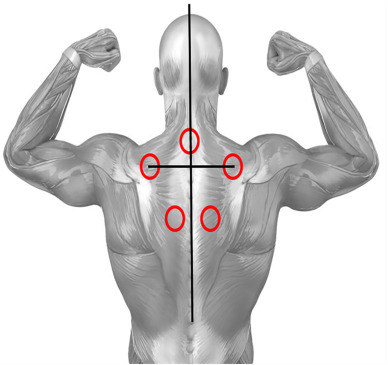
Cupping Therapy and Specific Autoimmune Diseases:
Some preliminary research suggests that cupping therapy may be particularly beneficial in certain autoimmune diseases:
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Several studies have reported improvements in pain and swelling among patients with rheumatoid arthritis following cupping sessions.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): There is anecdotal evidence and some small studies indicating that cupping may help alleviate some symptoms of lupus, though further research is needed.
Multiple Sclerosis: Research on cupping’s impact on multiple sclerosis is still limited, but some early studies suggest potential improvements in symptoms such as fatigue.
Cupping Therapy as a Complementary Treatment, Not a Substitute:
It is crucial to emphasize that cupping should not be considered a primary or substitute treatment for conventional medical therapies for autoimmune diseases. Cupping should be used as a complementary treatment under the guidance of a medical professional, alongside prescribed medications.
Cupping Therapy Research and Autoimmune Diseases: The Path Toward a Deeper Understanding:
Scientific research on the effects of cupping therapy on autoimmune diseases is still in its early stages. More high-quality studies are needed to identify the precise mechanisms of action, confirm its efficacy in treating various autoimmune diseases, and determine the optimal protocols for safe and effective application.
Unique Conclusion:
Cupping therapy offers a unique perspective and promising potential as a complementary treatment for patients with autoimmune diseases. It may help reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response, potentially leading to pain relief and improved quality of life. However, there remains a need for more high-quality scientific research. Autoimmune patients considering cupping therapy should consult their doctors and specialists to assess its suitability and integrate it safely into their overall treatment plan. Embracing an integrated approach that combines traditional and complementary therapies under medical supervision may offer new hope in managing these complex diseases.